
Tp fancontrol code#
The code lets you define a temperature range for each thermal sensor. # sudo echo "options thinkpad_acpi experimental=1 fan_control=1" >/etc/modprobe.d/thinkpad_nf On Ubuntu > 10.04 or from kernel 2.6.32 onwards: To make the kernel module settings permanent and to make them be executed at boot run below command and reboot afterwards: In Linux 2.6.22 and higher you need to additionally pass fan_control=1 to the module thinkpad_acpi (e.g., # modprobe thinkpad-acpi experimental=1 fan_control=1) It requires the ibm-acpi module to be loaded with the experimental=1 module parameter (e.g., # modprobe ibm_acpi experimental=1). This script works with any recent Linux kernel (2.6.14 and higher). Note that the fan levels, thresholds and anti-pulsing hacks are system-specific, so you may need to adjust them.Ĭomprehensive bash script with fine control over fan speed In addition, they include a hack for preventing the annoying fan pulsing that occurs on some systems.

The following scripts sets the fan speed according to the system's thermal sensors.
Tp fancontrol update#
The firmware doesn't update the sensors more than once every 2s, so care should be taken not to waste resources by reading them too often. It enables you to keep track of your system’s status and ensure temperatures do not exceed safe levels.Closed-loop fan control requires a thermal sensor sweep, which is an expensive operation. The latest command is displayed in the main window, and a complete log of temperature and fan speed data is also listed. It is also possible to select the preferred option directly from the application’s system tray menu.
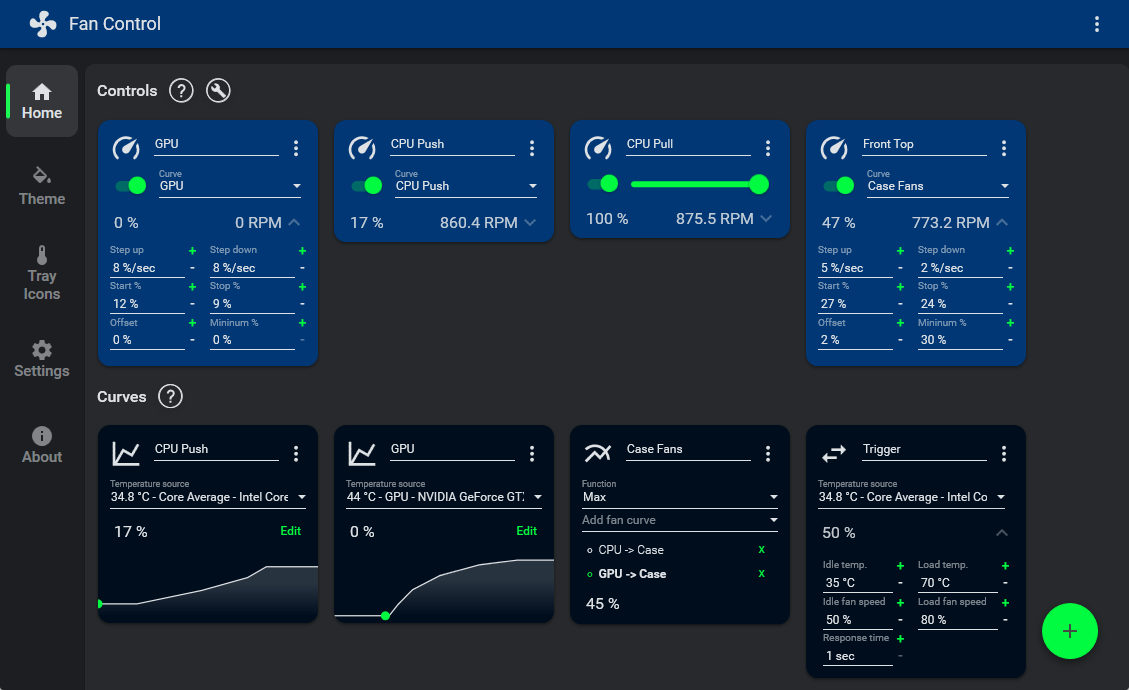
Tp fancontrol manual#
When using the manual mode, you can select one of the seven speed settings at any time. You can choose from three operating modes: BIOS, Smart and manual. It monitors multiple sensors, showing the temperature of your CPU, GPU, motherboard and more. Once launched, the program should display the current status of your notebook in regards to system temperature and fan speed. It enables users to manage fan speed in various ways in order to reduce noise levels. Thinkpad Fan Controller is an open-source utility designed to help users of notebooks from the Thinkpad T4x (T40/T41/T42/T43) series, which lack appropriate fan control mechanisms.
Tp fancontrol full#
If fans are running at full speed while your PC is idle, the noise can get very annoying. Computer fans can get quite loud when performing resource-intensive operations, and some older devices cannot increase or decrease fan speed based on the system’s temperature.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
